MACD and Moving Average Combo Trading Strategy

Trading strategies can often feel like navigating through a maze, especially when you’re trying to decipher complex indicators. However, the MACD and Moving Average Combo Trading Strategy is one approach that stands out for its simplicity and effectiveness. Let’s dive into the world of MACD and Moving Averages and explore how combining these two can be a game-changer for your trading journey.
What is the MACD?
The MACD, or Moving Average Convergence Divergence, is a momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It’s widely used among traders for spotting changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend.
Breaking Down the MACD Indicator
The MACD consists of three main components:
- MACD Line: The difference between the 12-day and 26-day Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs).
- Signal Line: A 9-day EMA of the MACD line.
- Histogram: A graphical representation showing the difference between the MACD line and the Signal line.
How the MACD Works
When the MACD line crosses above the Signal line, it suggests a bullish signal, indicating it might be a good time to buy. Conversely, when the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, it suggests a bearish signal, indicating it might be time to sell.
Key Components of the MACD
- Crossovers: The main buy/sell signals.
- Divergence: Indicates a potential reversal in the current trend.
- Rapid Rises/Falls: Indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
What are Moving Averages?
Moving averages smooth out price data to create a single flowing line that traders can use to identify the trend direction. They are one of the simplest and most effective technical indicators.
Types of Moving Averages
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The SMA is the most basic form of a moving average, calculated by adding the closing prices of a security for a given number of periods and then dividing by the number of periods.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
The EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information compared to the SMA. This quality makes the EMA a preferred choice for many traders.
Why Moving Averages are Important in Trading
Moving averages help traders determine the overall trend direction and can also be used to spot potential support and resistance levels. They are fundamental in forming the backbone of many trading strategies, including the MACD and Moving Average Combo.
Combining MACD with Moving Averages for a Powerful Strategy
The real magic happens when you combine the MACD with moving averages. This combo can help you confirm the signals you’re getting, ensuring you’re trading in line with the overall market trend.
The Synergy Between MACD and Moving Averages
Using moving averages alongside MACD can help validate entry and exit points. For instance, if the MACD gives a buy signal, but the price is below the 50-day moving average, you might want to wait until the price moves above the moving average to confirm the uptrend.
Benefits of Using This Combination in Trading
- Enhanced Signal Confirmation: Reduces false signals by providing an extra layer of confirmation.
- Trend Identification: Helps you stay on the right side of the market trend.
- Versatility: Can be used across different time frames and asset classes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing the MACD and Moving Average Combo Strategy
Ready to start trading with the MACD and Moving Average Combo? Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get going.
Setting Up Your Charts
- Open your trading platform and select your asset of choice.
- Add the MACD indicator to your chart.
- Add your preferred moving averages (e.g., 50-day SMA and 200-day SMA).
Choosing the Right Time Frames
Choosing the right time frame is crucial. For day trading, you might use shorter time frames like the 15-minute or hourly charts. For swing trading, daily charts are more appropriate.
Identifying Entry and Exit Points
- Entry Point: Look for a bullish MACD crossover with price above the moving averages.
- Exit Point: Consider exiting when the MACD shows a bearish crossover or when the price falls below the moving averages.
Risk Management Tips
- Always set a stop-loss below recent lows to protect your capital.
- Use position sizing to ensure no single trade can significantly impact your portfolio.
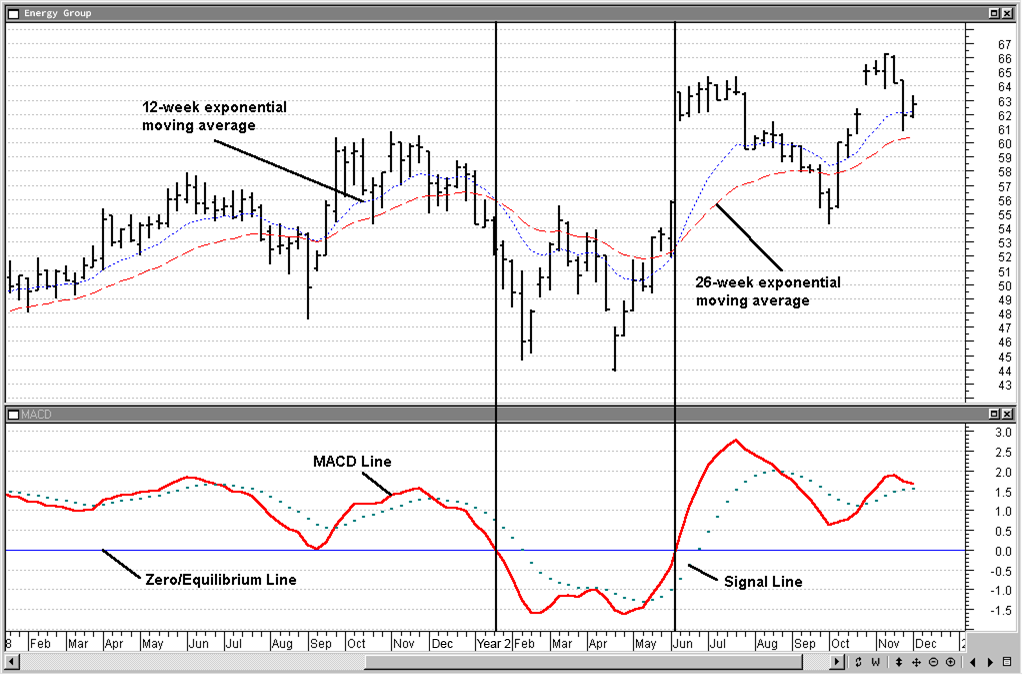
Picture 1 shows the relationship between the two moving average lines and the MACD for the hypothetical Energy Group. At the top of the chart, you’ll see the weekly price plots for Energy Group along with two key moving averages: the 12-week and 26-week exponential moving averages. Down at the bottom, we have the MACD line, the signal line, and the all-important equilibrium (or zero) line.
Now, there are a couple of things that really jump out when you look at this chart. First, notice that when the 12-week and 26-week moving averages start to drift apart, the MACD line heads upward. It’s like they’re playing tug-of-war, and the MACD line rises when the averages are far apart. Second, when these moving averages cross each other, the MACD line mirrors that by crossing the equilibrium line at the same time. You can spot these moments because they’re highlighted with vertical lines on the chart.
For instance, in the week ending January 22 of Year 2, the MACD line dipped below the equilibrium line right when the 12-week moving average crossed below the 26-week average. Then, fast forward to the week ending June 4 of Year 2, and you’ll see the opposite: the 12-week average climbed above the 26-week, and the MACD line followed suit, crossing above the equilibrium line. Pretty neat, right? This interplay is a great visual cue for understanding momentum shifts in the market.
Best Practices for the MACD and Moving Average Combo Strategy
To get the most out of this strategy, it’s important to follow some best practices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring the Overall Trend: Make sure the MACD signals align with the broader market trend.
- Overtrading: Stick to clear signals and avoid forcing trades.
- Poor Risk Management: Always have a risk management plan in place.
Fine-Tuning the Strategy for Better Results
You might need to tweak the moving average periods or MACD settings based on the asset you’re trading and the time frame you prefer. Testing and optimizing can greatly enhance your strategy’s performance.
Real-Life Examples of the MACD and Moving Average Combo Strategy
Let’s explore a couple of real-life scenarios where this strategy can be applied.
Case Study 1: Bullish Market Scenario
In a bullish market, the price of an asset might be trending above the moving averages with the MACD line crossing above the Signal line. This could be a strong buy signal, especially if the trend is supported by high volume.
Case Study 2: Bearish Market Scenario
In a bearish scenario, the price might be trending below the moving averages, with the MACD line crossing below the Signal line. This would suggest a sell or shorting opportunity, aligning with the downtrend.
Pros and Cons of the MACD and Moving Average Combo Strategy
Advantages of the Strategy
- Simple to Use: Even beginners can grasp the basics of this strategy.
- Effective Across Markets: Can be applied to stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
- Flexible: Works on multiple time frames.
Potential Drawbacks to Consider
- Lagging Indicators: Both MACD and moving averages are lagging indicators, which means they can sometimes give delayed signals.
- False Signals: In choppy markets, the strategy might produce false signals, leading to potential losses.
Conclusion
The MACD and Moving Average Combo Trading Strategy is a versatile and powerful approach that can help traders navigate the markets with more confidence. By combining the momentum insights of MACD with the trend-confirming power of moving averages, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve their overall trading performance. Remember, no strategy is foolproof, and the key to success lies in testing, adapting, and continuously learning from the markets.
FAQs
- What markets can I use the MACD and Moving Average Combo Strategy in?
You can use this strategy in various markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
- How often should I adjust my moving averages?
Adjust your moving averages based on your trading style and the time frame you’re using. Regular review and backtesting can help you find the optimal settings.
- Can beginners use this strategy?
Yes, this strategy is beginner-friendly due to its simplicity and the clear signals it provides.
- What are the best time frames for this strategy?
The best time frames depend on your trading style. Day traders might prefer shorter time frames, while swing traders often use daily charts.
- How do I know if the MACD signal is strong enough to act on?
Look for strong crossovers accompanied by supporting trends and volume. Confirming signals with moving averages can also enhance the strength of the MACD signal.


